Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to the diabetic diet! If you’re someone who has diabetes, managing your blood sugar can be a real challenge. The good news is that, with the right diet and lifestyle choices, it is possible to live a healthy and happy life with diabetes. This guide will provide you with all the information you need to manage your blood sugar effectively and ensure a healthy and stable life. So, let’s dive in!
Understanding Diabetes and Blood Sugar
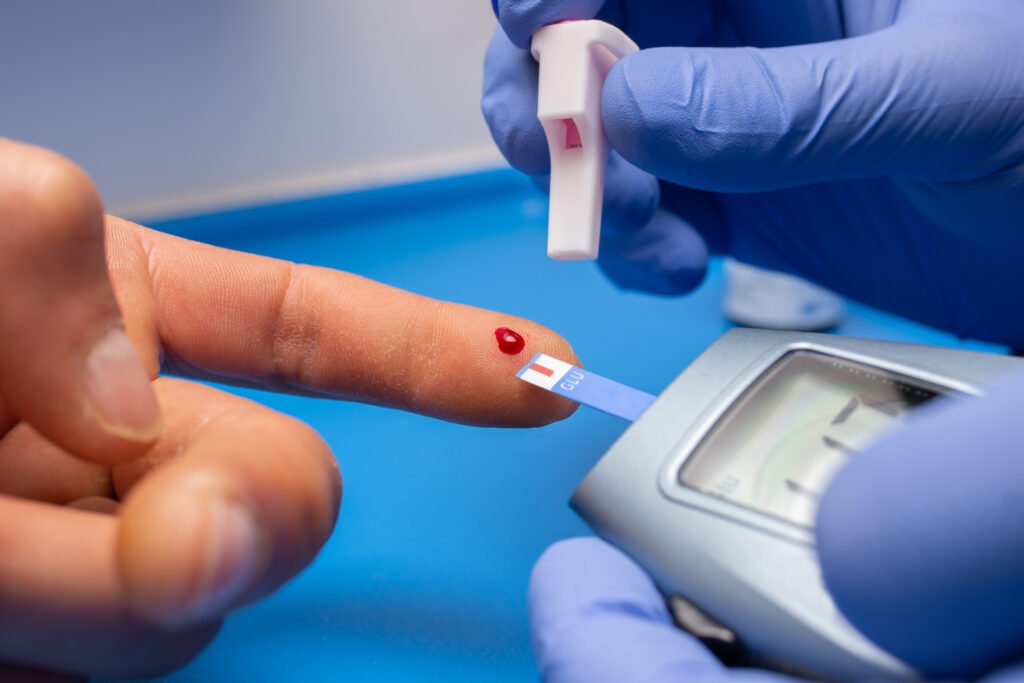
Managing blood sugar levels is vital for individuals with diabetes, and it all starts with a well-planned diabetic diet. In this comprehensive guide to a diabetic diet, we’ll cover everything from understanding diabetes and blood sugar to meal planning and medication management.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes glucose. There are two types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, and Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body can’t use insulin properly. Regardless of the type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are affected. High blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can result in symptoms such as thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels, also known as hypoglycemia, can result in symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion. It’s important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly. This helps identify patterns and adjust the diabetic diet, exercise routine, or medication accordingly. In the next section, we’ll cover the symptoms and causes of high and low blood sugar levels.
Symptoms and Causes of High and Low Blood Sugar

High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, occurs when the body doesn’t have enough insulin or can’t use it properly. Symptoms of high blood sugar include frequent urination, blurred vision, increased thirst, fatigue, and headaches. It can be caused by factors such as overeating, lack of physical activity, stress, and illness.
On the other hand, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when the blood sugar drops below a normal range. Symptoms of low blood sugar include confusion, rapid heartbeat, sweating, dizziness, hunger, and weakness. It can be caused by factors such as insulin overdose, skipping meals, excessive physical activity, and certain medications.
It’s important to note that individuals can experience both high and low blood sugar levels, and symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the condition. To manage blood sugar levels, individuals must monitor their blood sugar regularly, take prescribed medications, and follow a diabetic diet. It’s important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
The Importance of a Diabetic Diet

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people globally. One of the essential components of managing diabetes is following a proper diet plan. A diabetic diet can help control your blood sugar levels, manage your weight, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at managing blood sugar through diet and other lifestyle changes. The hormone insulin helps your body use glucose for energy. In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use its insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. A diabetic diet is a healthy eating plan that focuses on controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. A balanced, diabetic-friendly diet can help manage weight, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
What is a diabetic diet?
A diabetic diet focuses on foods that are low in sugar and rich in nutrients. It typically includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Portion control is also crucial in a diabetic diet. Benefits of a Diabetic Diet Following a diabetic diet can have numerous health benefits, including stabilized blood sugar levels, weight loss, lower blood pressure, and a reduced risk of heart disease. Additionally, eating a well-balanced diet can provide you with more energy and help you feel better overall. Foods to Avoid on a Diabetic Diet To manage their blood sugar levels, people with diabetes should limit their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-carb snacks.
Foods to Include in a Diabetic Diet
A diabetic diet should include nutrient-dense foods such as whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean protein sources, and healthy fats like omega-3s. Good protein options include fish, poultry, eggs, and legumes. Meal Planning for Diabetics Meal planning is crucial to managing blood sugar levels. Planning ahead helps to ensure that you’re eating healthy food in the right portions. Some popular meal-planning methods include the plate method, counting carbohydrates, and reading food labels. Speak to a registered dietician to learn more about the best meal planning options for you.
Read Only: Knee Pain When Bending: Causes and Exercises for Relief
Meal Planning for Diabetics

It is essential to keep a watchful eye on what you eat and how much you eat. Diabetic meal planning is not rocket science if you have the right meal plan in hand. It can significantly reduce the risk of high or low blood sugar levels and, in turn, help manage diabetes better. Undoubtedly, meal planning can be a time-consuming and challenging task, but you know what? It’s worth it! A little bit of planning and effort can go a long way toward maintaining overall health. Now, let’s have a look at some of the key points to keep in mind when meal planning for diabetics.
The plate method of meal planning is an excellent technique. Fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with low-glycemic-index carbohydrates. This method keeps your blood sugar levels in check and ensures a well-balanced diet.
Counting carbohydrates is an essential aspect of diabetic meal planning. It is crucial to keep track of the number of carbohydrates you consume during the day. Carbohydrates have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Therefore, it is essential to limit your carb intake, especially if you’re diabetic. Also, always make sure to read food labels. Knowing what’s in your food can help you determine if it’s safe and healthy to consume. Don’t forget to glance at the total carbohydrates per serving.
Exercise and Blood Sugar Management
Exercise is an essential component of blood sugar management for diabetics. It helps in reducing blood sugar levels, lowering body weight, and improving insulin sensitivity. For diabetics, regular exercise should be a part of their daily routine. Low-intensity exercises such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are suitable for most diabetics. High-intensity workouts like weightlifting can also be beneficial but require medical supervision.
The impact of exercise on blood sugar levels can vary depending on several factors, such as the type and duration of exercise and the timing of food and medication ingestion. It’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to determine how it impacts the levels.
However, it’s essential to consider your physical capabilities when choosing the type of exercise. Pushing yourself beyond your limitations can cause adverse effects. Take small steps and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the workouts.
In conclusion, regular exercise is crucial for managing blood sugar levels in diabetics. It’s not only beneficial for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels but also for overall health and wellness. So, stay active and stay healthy!
Managing Blood Sugar with Medication

For some diabetics, managing blood sugar levels with diet and exercise alone may not be enough. That’s where medication comes in. There are several types of medication that can be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels in diabetics.
One type is insulin injections, which are typically used for type 1 diabetes but may also be used in certain cases for type 2 diabetes. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells, where it can be used for energy.
Another type of medication is oral diabetes medication, which is typically used for type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways to lower blood sugar levels by either helping the body to use insulin more effectively or by inhibiting the production of glucose in the liver. It’s crucial to take diabetic medication as prescribed by a doctor, as improper use can lead to dangerous fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
It’s also important to be aware of potential side effects, which can vary depending on the medication. Some common side effects of diabetic medication include nausea, diarrhea, and weight gain. More serious side effects may include low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) or high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), which can be life-threatening if not properly managed. Medication can be a powerful tool in managing blood sugar levels for diabetics, but it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to ensure that the right type and dosage are prescribed.
Diabetic Diet NHS:

A diabetic diet is a crucial component in managing diabetes and promoting overall health. The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom provides valuable guidance on creating a balanced and sustainable eating plan for individuals with diabetes. Let’s delve into the key principles of the diabetic diet as recommended by the NHS.
Understanding the Diabetic Diet NHS:
Balanced Carbohydrates: The NHS emphasizes the importance of balancing carbohydrate intake, a key factor in blood sugar management. Instead of eliminating carbohydrates entirely, the focus is on choosing complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index. Foods such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables provide a steady release of glucose, helping to avoid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Portion Control: Portion control plays a crucial role in managing calorie intake and stabilizing blood sugar levels. The NHS recommends paying attention to portion sizes and spreading meals throughout the day to prevent overeating and better regulate blood glucose.
Healthy Fats: Incorporating healthy fats into the diet is encouraged. Foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can contribute to heart health without adversely affecting blood sugar levels.
Lean Proteins: Including lean proteins in meals is essential for maintaining muscle mass and promoting satiety. Options like fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes are recommended by the NHS, providing a diverse range of nutrients without excess saturated fats.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber aids in digestion and helps control blood sugar levels. The NHS suggests incorporating a variety of high-fiber foods, like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, into the diet to support overall health and diabetes management.
Limiting Sugar and Processed Foods: Minimizing the intake of sugary foods and processed snacks is a key aspect of the diabetic diet. The NHS advises individuals to be mindful of added sugars in their diet, opting for natural sources of sweetness when necessary.
Diabetic Diet: Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetics. By understanding diabetes and blood sugar levels, recognizing high and low blood sugar symptoms, following a diabetic diet, and incorporating exercise and medication, one can effectively manage blood sugar levels.
Following a healthy and balanced diabetic diet can significantly improve blood sugar levels. Meal planning plays a vital role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. It is also essential to exercise regularly, as it helps with weight management, reduces the risk of heart disease, and improves blood sugar levels.
In addition to a healthy diet and regular exercise, medication may be necessary in some cases. However, it is essential to follow the guidance of a medical professional when managing blood sugar levels with medication. By adopting these lifestyle habits, individuals with diabetes can have greater control over their blood sugar levels, leading to a healthier and more fulfilled life. So, start taking care of your diet and exercise now, and stay healthy!
