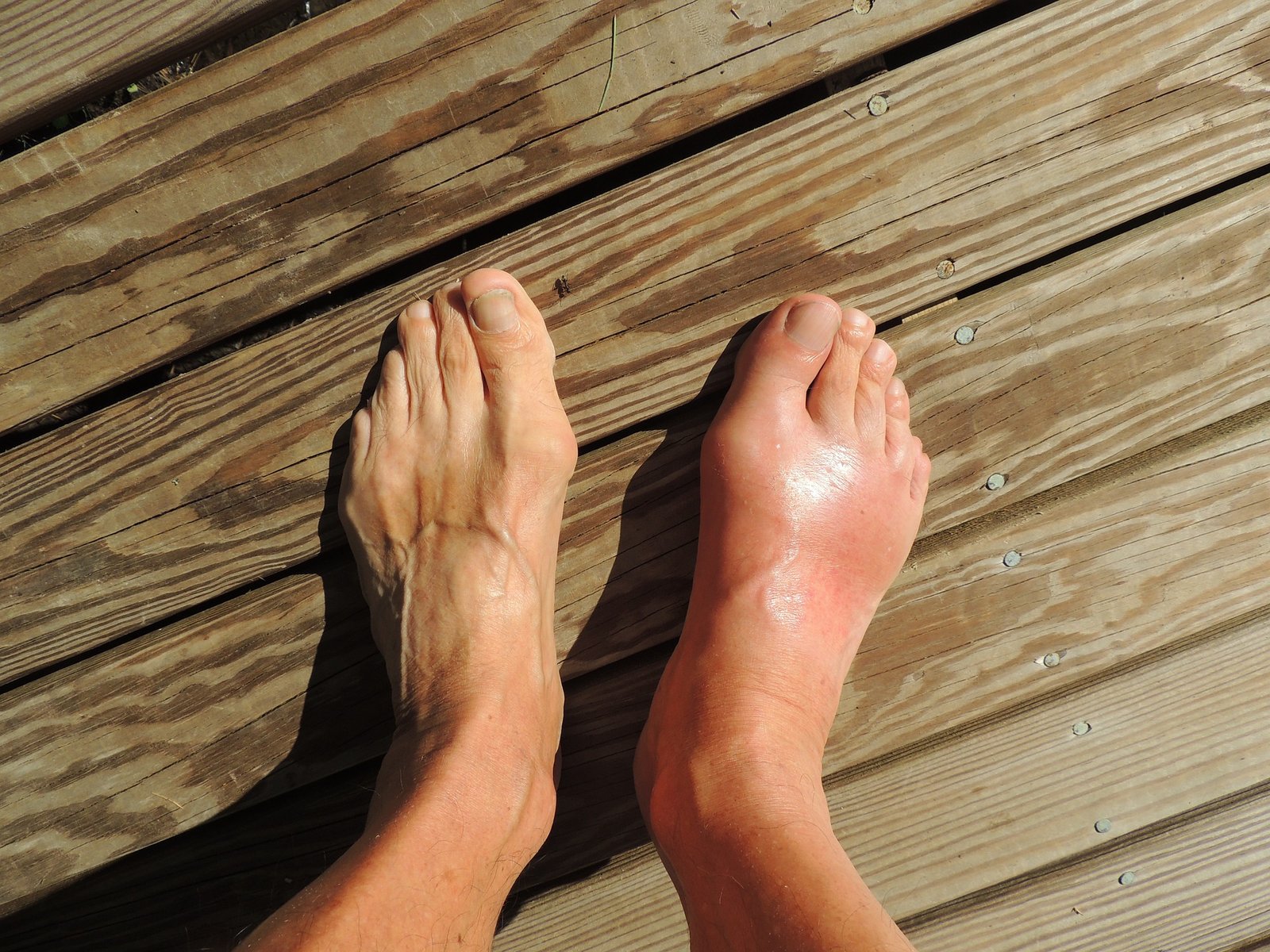
Introduction
Gout, often referred to as the “disease of kings,” is a form of inflammatory arthritis that has persisted through centuries, leaving its mark on the pages of medical history. This ancient malady has been recognized since the time of Hippocrates, with its distinct symptoms and painful manifestations affecting individuals from various walks of life. Caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, gout presents itself as more than just a physical affliction; it embodies a delicate interplay between lifestyle, genetics, and metabolic factors. Despite its historical prominence, the understanding of gout continues to evolve, with modern research shedding light on novel therapeutic approaches and lifestyle interventions. As we delve into the intricate tapestry of gout, it becomes apparent that this age-old ailment is not merely a relic of the past but a dynamic challenge that requires a nuanced comprehension and a comprehensive approach for effective management in the present day.
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Crystalized Pain
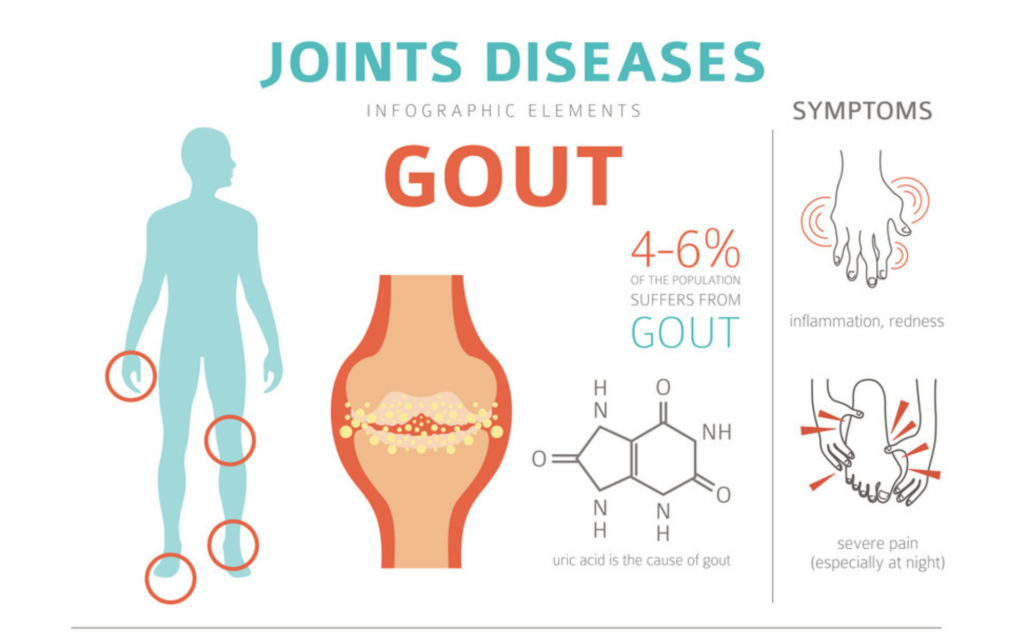
Gout, often referred to as the “disease of kings” or the “rich man’s disease,” is a form of arthritis that has plagued humanity for centuries. Despite its historical associations, it is not exclusive to any particular social class and can affect anyone. This complex and painful condition is characterized by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joints, leading to intense bouts of pain and inflammation. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of gout, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective management strategies.
Understanding the Culprit: Urate Crystals
Gout is primarily caused by the buildup of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is a natural byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and produced by the body. When the level of uric acid in the blood exceeds the body’s ability to eliminate it, urate crystals form and accumulate in the joints, triggering the inflammatory response characteristic of gout.
The Dance of Symptoms:
It often manifests as sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected joints. The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, although gout can also target other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. These acute episodes, also known as flares, can last for days or weeks, making it challenging for individuals to carry out their daily activities.
Risk Factors and Triggers:
While hyperuricemia is the underlying cause of gout, certain risk factors and triggers can contribute to the development of the condition. These include a diet rich in purine-containing foods (such as red meat, seafood, and organ meats), excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, genetics, and certain medical conditions or medications. Understanding these risk factors can empower individuals to make lifestyle changes that may help prevent gout or manage its symptoms more effectively.
Diagnosing Gout:
Diagnosing this involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and laboratory tests. During a gout attack, a healthcare professional may extract fluid from the affected joint to examine for the presence of urate crystals. Blood tests measuring uric acid levels can also provide valuable information, although they alone may not be conclusive, as some individuals with gout may have normal uric acid levels between flares.
Management and Prevention:
Managing gout requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both acute flares and long-term prevention. Treatment options may include medications to relieve pain and inflammation, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids. Additionally, medications that lower uric acid levels, like allopurinol or febuxostat, may be prescribed for chronic management.
Preventive measures focus on lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes to reduce purine intake, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated. Regular physical activity can also contribute to overall well-being and may help prevent gout attacks.
The Road to Better Joint Health:
Understanding gout is essential for those affected and their healthcare providers. With the right knowledge and proactive measures, individuals can effectively manage this disease, minimize the frequency and severity of flares, and improve their overall joint health. As ongoing research continues to shed light on the intricacies of this ancient ailment, new treatments and preventive strategies may offer even greater hope for those grappling with the crystalized pain of gout.
Unveiling the Pitfalls: Common Gout Management Mistakes

A form of inflammatory arthritis can be an unwelcome intruder, causing intense pain and discomfort. Managing this condition requires diligence and a strategic approach. Unfortunately, there are common pitfalls that individuals often stumble into when dealing with gout. Recognizing these mistakes is the first step towards effective management.
Neglecting Hydration
One of the most common mistakes in it’s management is overlooking the importance of hydration. Water plays a crucial role in flushing out uric acid, the culprit behind gout attacks. Dehydration can lead to an accumulation of uric acid crystals, increasing the risk of flare-ups. Individuals with gout should make a conscious effort to maintain adequate fluid intake.
Ignoring Dietary Choices
Gout is intricately linked to diet, and certain foods can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Some people make the mistake of ignoring dietary recommendations and consuming high-purine foods like red meat, organ meats, and shellfish. Balancing the intake of purine-rich foods with low-purine alternatives, such as vegetables and whole grains, is crucial for it’s effective management.
Overlooking Medication Adherence
Consistency is key when it comes to medication in gout management. Skipping doses or discontinuing medications prematurely can lead to a resurgence of symptoms. It’s vital to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan, as medications are designed to control uric acid levels and prevent future attacks.
Underestimating the Role of Lifestyle:
While medication is a fundamental aspect of gout management, lifestyle modifications should not be underestimated. Lack of exercise, excess alcohol consumption, and stress can contribute to gout flare-ups. Regular physical activity, moderation in alcohol consumption, and stress management techniques are integral components of a holistic gout management strategy.
Delaying seeking professional help
Some individuals try to self-diagnose or self-treat gout symptoms, often resorting to over-the-counter remedies without consulting a healthcare professional. Delaying proper medical attention can lead to more severe complications. Seeking timely advice from a healthcare provider ensures an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Read Also: Bacterial Vaginosis Demystified: Expert-Approved Solutions
Mastering Effective Gout Management
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, most commonly affecting the big toe. While it can be a debilitating condition, mastering it’s effective management is key to mitigating symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Understanding the Culprit: Uric Acid
Gout is primarily triggered by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, which are found in certain foods and are also produced by the body. Effective management starts with understanding and addressing the root cause: elevated uric acid levels.
Dietary Changes
One of the cornerstones of gout management is adopting a gout-friendly diet. Limiting the intake of high-purine foods such as organ meats, seafood, and sugary beverages can help lower uric acid levels. Embracing a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products can contribute to an overall healthier lifestyle and aid in gout control.
Hydration Matters
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for gout sufferers. Adequate water intake helps flush out excess uric acid from the body, reducing the likelihood of crystal formation in the joints. Individuals with gout should aim for at least eight glasses of water per day, and even more during gout attacks.
Medication Adherence
Pharmacological interventions play a significant role in managing it effectively. Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and xanthine oxidase inhibitors are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and lower uric acid levels. Adhering to prescribed medications is vital for preventing flare-ups and maintaining long-term joint health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond diet and medication, certain lifestyle changes can contribute to effective gout management. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight can exacerbate it’s symptoms. Regular exercise, particularly low-impact activities like swimming or walking, can help improve joint function and reduce the risk of recurrent attacks.
Regular Monitoring and Consultation
Gout management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels through blood tests and open communication with healthcare providers are essential. Adjustments to medications or lifestyle recommendations may be necessary based on individual responses and changes in health status.
The Holistic Approach
Mastering effective gout management involves adopting a holistic approach that combines dietary modifications, hydration, medication adherence, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring. By addressing the root causes and managing symptoms comprehensively, individuals with gout can regain control over their lives and minimize the impact of this challenging condition.
Case Studies: Learning from Mistakes

Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, has been a subject of medical scrutiny for centuries. Despite advancements in understanding and treatment options, managing gout remains a challenge due to its complex nature. Examining real-life case studies can provide invaluable insights into the nuances of gout management and help healthcare professionals learn from both successes and mistakes.
Neglecting Lifestyle Modifications
Mr. A, a middle-aged man with a history of gout attacks, sought medical attention after experiencing recurrent flares. Despite being prescribed medications to control uric acid levels, Mr. A neglected crucial lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and increased water intake. The oversight led to continued uric acid buildup, resulting in persistent gout attacks. This case underscores the importance of patient education and the need for a holistic approach, incorporating both medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Overlooking Comorbidities
Mrs. B, a diabetic patient, developed gout symptoms that were initially misattributed to her existing health condition. The oversight delayed the diagnosis and initiation of appropriate gout management. This case highlights the significance of considering comorbidities in gout diagnosis, as conditions like diabetes may complicate the treatment plan. A thorough medical history and comprehensive evaluation are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Inadequate Monitoring of Medication Adherence
Mr. C, a gout patient prescribed medication to control uric acid levels, experienced recurrent flares despite apparent compliance. Further investigation revealed inconsistent medication adherence, leading to suboptimal control of uric acid. This case emphasizes the necessity of regular follow-ups and open communication between healthcare providers and patients. Monitoring medication adherence ensures the effectiveness of treatment plans and helps prevent gout exacerbations.
Delayed Adjustment of Treatment
Ms. D, a young woman with gout, initially responded well to medication. However, over time, her uric acid levels started to rise, and gout attacks became more frequent. A delayed adjustment of her treatment plan allowed the disease to progress unchecked. This case underscores the importance of proactive monitoring and timely adjustments to treatment plans. Regular assessments help healthcare providers adapt strategies to the evolving nature of gout and prevent long-term complications.
Navigating the Path to Relief Through Professional Guidance
While there’s a plethora of information available online about managing gout, seeking professional guidance is paramount for effective treatment and long-term relief.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals:
Accurate Diagnosis:
Gout symptoms can mimic those of other conditions, making an accurate diagnosis crucial. Healthcare professionals, equipped with their expertise, can distinguish between gout and other joint-related issues, ensuring the right course of action.
Tailored Treatment Plans:
Every individual is unique, and so is their experience with gout. Consulting healthcare professionals allows for personalized treatment plans that consider factors such as overall health, lifestyle, and specific triggers.
Medication Management:
Prescription medications are often necessary to manage this effectively. Only healthcare professionals can prescribe and monitor the appropriate medications, adjusting them as needed to achieve optimal results while minimizing potential side effects.
Role of Rheumatologists in Gout Management:
Specialized Expertise:
Rheumatologists are specialists in the field of arthritis and related conditions. Their in-depth knowledge of gout enables them to provide precise diagnoses and customized treatment strategies.
Long-Term Management:
Gout is a chronic condition, and rheumatologists play a vital role in long-term management. They can help patients understand the importance of lifestyle modifications, monitor disease progression, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Prevention of complications:
Left untreated, gout can lead to complications such as joint damage and kidney stones. Rheumatologists are skilled at identifying potential risks and implementing preventative measures to safeguard the patient’s overall health.
A Collaborative Approach Between Patients and Healthcare Providers:
Open Communication:
Establishing clear and open communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential. Patients should openly share their symptoms, concerns, and any challenges they face in managing the condition.
Shared Decision-Making:
A collaborative approach involves both the patient and the healthcare team actively participating in decision-making. This empowers patients to take ownership of their health while benefiting from the guidance and expertise of professionals.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Gout management often involves lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments and exercise. Collaborating with healthcare providers allows for realistic goal-setting and ongoing support as patients work towards healthier habits.
Gout NHS: Understanding, Management, and Lifestyle Tips
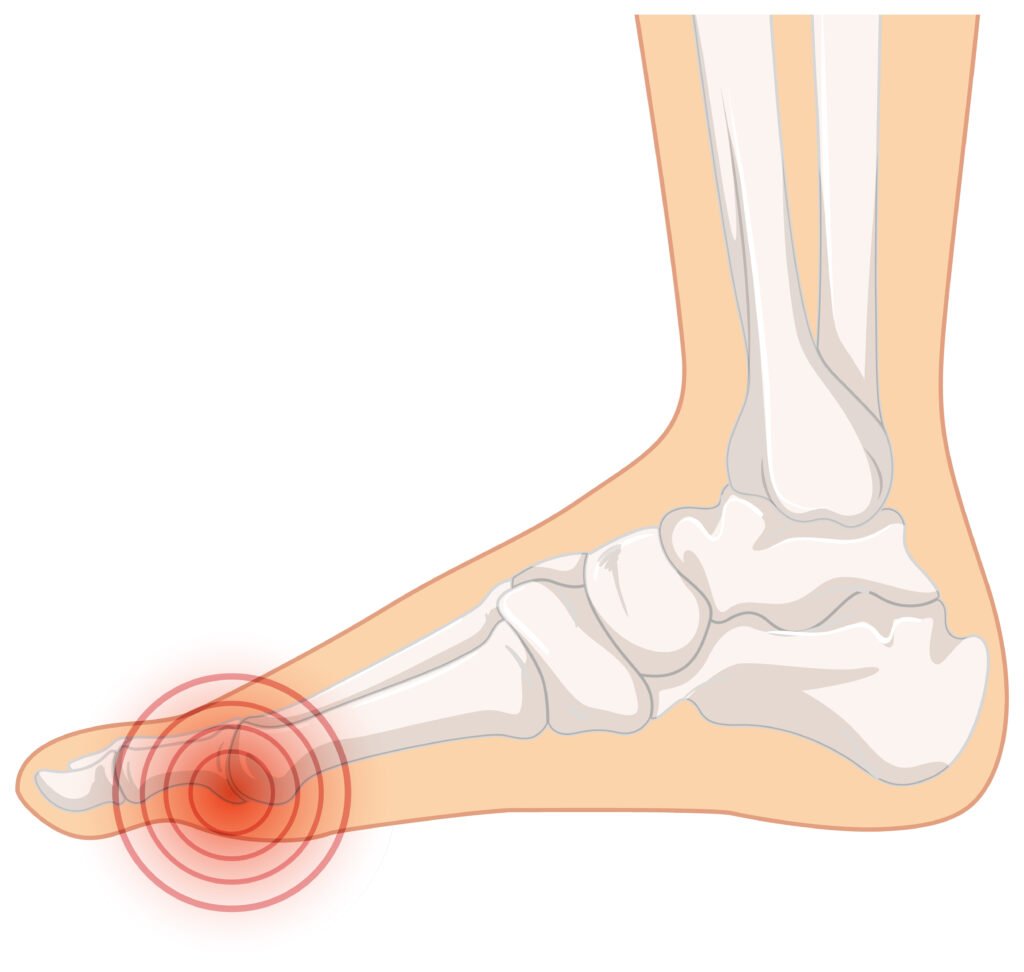
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, is a condition that arises from the deposition of uric acid crystals in joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, and redness. The National Health Service (NHS) plays a pivotal role in educating individuals about the nuances of gout, encompassing both understanding and management strategies. The NHS guidelines emphasize the importance of comprehending the underlying causes of gout, such as genetics, diet, and lifestyle factors. By fostering a deeper understanding, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps towards prevention. The management aspect delves into pharmacological interventions, including medications that lower uric acid levels and alleviate symptoms. However, the NHS doesn’t stop there; it extends its support to the realm of lifestyle modifications. Dietary recommendations, such as reducing purine-rich foods and maintaining a healthy weight, are integral components of the NHS approach to managing gout. Furthermore, the NHS provides valuable insights into lifestyle adjustments, urging individuals to stay hydrated, limit alcohol consumption, and engage in regular physical activity. By adopting a holistic approach that combines education, medical intervention, and lifestyle adjustments, the NHS empowers individuals to take charge of their gout management, fostering a better quality of life and long-term well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, the journey to effective gout management is a nuanced one, requiring a holistic perspective that incorporates various facets of lifestyle, medication, and holistic strategies. As we recap the key points discussed throughout this exploration, it becomes evident that understanding the intricacies of gout involves more than just addressing acute attacks—it’s about adopting a proactive stance towards long-term well-being. Beyond the conventional emphasis on medication, lifestyle modifications emerge as pivotal contributors to success in pain management. This entails a mindful approach to diet, exercise, and stress management. However, it’s crucial not to overlook the significance of collaboration with healthcare professionals, as their expertise and guidance can provide tailored solutions for individual cases.
In conclusion, let this be an encouragement for individuals to embrace the knowledge gained, empowering them to make informed decisions that transcend the challenges posed by gout. By cultivating resilience, learning from past experiences, and staying abreast of evolving therapies, each person can embark on a journey towards a healthier and more fulfilling life despite the complexities of gout. It’s not just about managing symptoms; it’s about crafting a lifestyle that fosters lasting well-being.