Introduction
The human body, a remarkable and intricate system, is often subjected to various external threats that challenge its ability to defend itself. Among these challenges, viral infections stand out as formidable adversaries, capable of disrupting the delicate balance within the body. One intriguing manifestation of viral infections is the development of rashes. This comprehensive exploration aims to delve into the intricate world of viral rash infections, shedding light on their symptoms, causes, and effective treatment strategies.
Common Viral Rash Infections
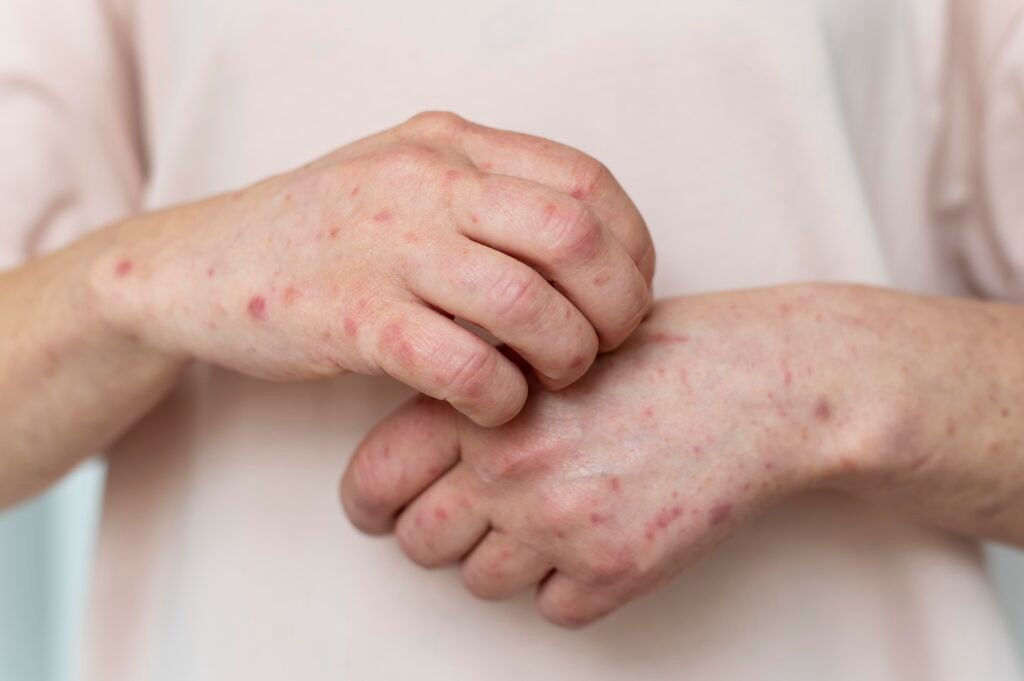
Measles (Rubeola):
Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus. The characteristic measles rash typically starts as flat red spots that gradually merge to form larger, raised patches. It often begins on the face and spreads down the body. Other symptoms may include fever, cough, and a runny nose.
Chickenpox (Varicella):
The Varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox, a contagious disease that results in an itchy rash with red spots and fluid-filled blisters. The rash usually starts on the face and trunk before spreading to other parts of the body. Although most common in children, chickenpox can affect individuals of any age.
Rubella (German Measles):
Rubella is caused by the rubella virus and is characterized by a mild rash that starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body. This infection is generally milder than measles but can be concerning for pregnant women as it may lead to congenital rubella syndrome in the unborn child.
Fifth Disease (Parvovirus B19):
The fifth disease is a viral infection caused by parvovirus B19. It often begins with a mild fever and flu-like symptoms, followed by a distinctive “slapped cheek” facial rash. The rash can then spread to the trunk and limbs, resulting in a lace-like pattern.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD):
HFMD is primarily caused by the coxsackievirus, and it commonly affects young children. The characteristic rash includes red spots and sores on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. It is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with infected individuals.
Identifying Symptoms of Viral Rash Infections

Viral infections can manifest in various ways, and one common yet often misunderstood symptom is the viral rash. These rashes can be caused by a wide array of viruses, ranging from the common cold to more serious infections like measles or chickenpox. Recognizing the symptoms of a viral rash infection is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the key indicators of viral rash infections, shedding light on the signs that should not be ignored.
Skin redness and inflammation:
The hallmark of a viral rash is often redness and inflammation on the skin. This can present as diffuse redness or as raised, bumpy areas. The extent and pattern of redness can vary depending on the specific virus causing the infection.
Fever:
Many viral infections go hand in hand with fever, and a viral rash is no exception. The body’s immune response to the virus can lead to an increase in body temperature, which is often accompanied by sweating and discomfort.
Itching or Irritation:
Viral rashes are notorious for causing itching and irritation. This discomfort is a result of the body’s inflammatory response to the virus, and scratching the affected area can exacerbate the rash and potentially lead to secondary infections.
Distribution Patterns:
Different viruses may exhibit characteristic distribution patterns on the skin. For instance, the measles virus often causes a red, blotchy rash that starts on the face and then spreads downward. Chickenpox, on the other hand, typically starts on the trunk and then spreads to the extremities.
Rash Appearance:
Viral rashes can take on various appearances, including maculopapular rashes (small, raised bumps), vesicular rashes (fluid-filled blisters), or petechial rashes (small red or purple spots). The type of rash can provide valuable clues about the underlying viral infection.
Respiratory Symptoms:
In many cases, viral rash infections are accompanied by respiratory symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, and a runny nose. This is especially true for viruses like the common cold or the influenza virus.
Systemic Symptoms:
Beyond skin and respiratory symptoms, viral infections can cause systemic symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, and malaise. These symptoms are indicative of the body’s efforts to combat the viral invader.
Duration of symptoms:
While some viral rashes resolve on their own within a few days, others may persist for a longer period of time. Monitoring the duration of symptoms can help healthcare professionals determine the severity of the infection and the appropriate course of action.
Read Also: Unusual Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Beyond the Joints
Causes of Viral Rash Infections
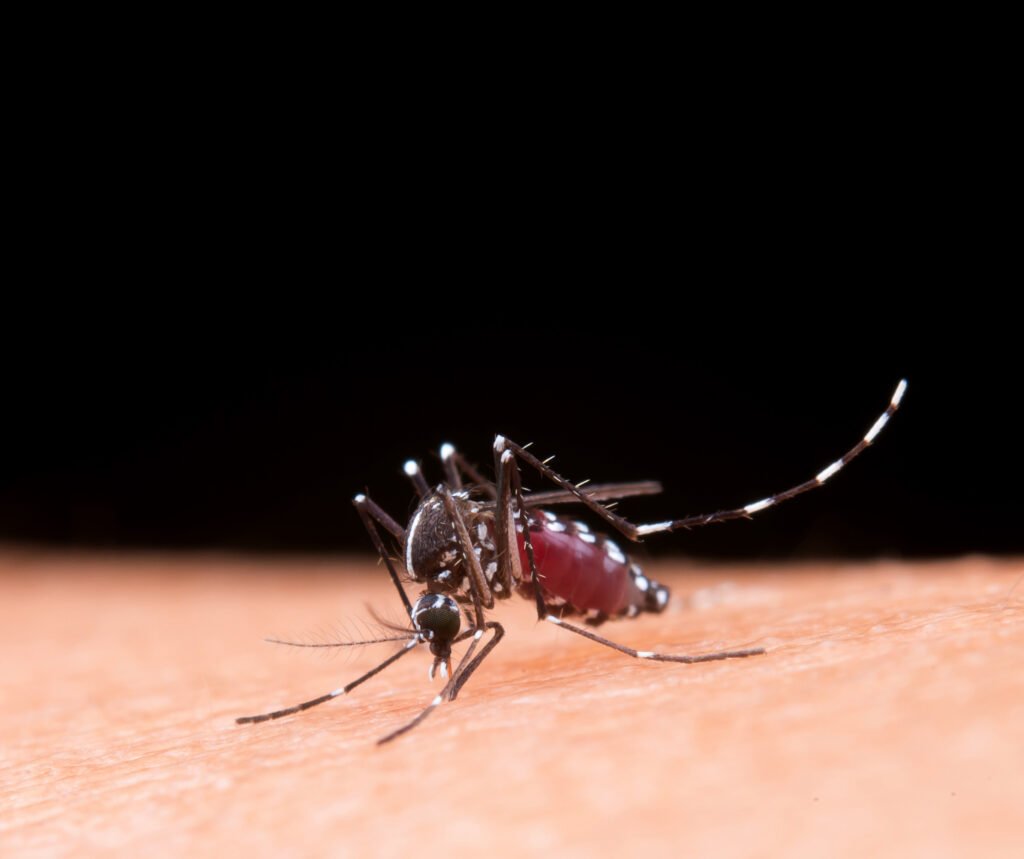
The human body is a complex system constantly under threat from various pathogens, including viruses. One intriguing manifestation of viral infections is the appearance of rashes on the skin. These viral rash infections can range from mild to severe, often causing discomfort and concern for those affected. Understanding the causes of these rashes is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. In this section, we will explore the diverse array of viruses that can lead to skin rashes and delve into the mechanisms behind their manifestation.
Common Viruses and Their Rash-Inducing Abilities:
Herpesviruses:
Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): This virus is responsible for chickenpox during childhood and shingles in adulthood. Both conditions are characterized by itchy, blister-like rashes.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV can cause painful cold sores or genital herpes, often accompanied by localized rashes and blisters.
Rubella Virus:
The rubella virus, also known as the German measles virus, can lead to a distinctive rash. It usually starts on the face and then spreads to the trunk and limbs.
Measles Virus:
Measles is notorious for its characteristic red, blotchy rash that typically begins on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body.
Parvovirus B19:
This virus can cause erythema, commonly known as a fifth disease. The associated rash often presents as bright red cheeks and a lacy rash on the arms, legs, and trunk.
Enteroviruses:
Coxsackievirus and echovirus, both members of the enterovirus family, can cause hand, foot, and mouth disease. This illness is marked by a rash on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth.
Mechanisms of Rash Formation:
Viral rash infections result from the body’s immune response to the invading virus. Several mechanisms contribute to the development of rashes:
Immune Response:
The immune system recognizes the presence of the virus and mounts a defense, releasing various chemicals and triggering inflammatory responses.
Vasculitis:
Some viruses can directly damage blood vessels, leading to vasculitis. This inflammation of blood vessels can manifest as a rash due to the impaired blood flow.
Cytokine Release:
Viral infections often induce the release of cytokines, signaling molecules that regulate immune responses. Excessive cytokine release can contribute to the development of rashes.
Viral Replication in Skin Cells:
Certain viruses replicate within skin cells, causing cell damage and triggering the release of inflammatory substances, leading to rash formation.
Treatment and Management of Viral Rash Infections
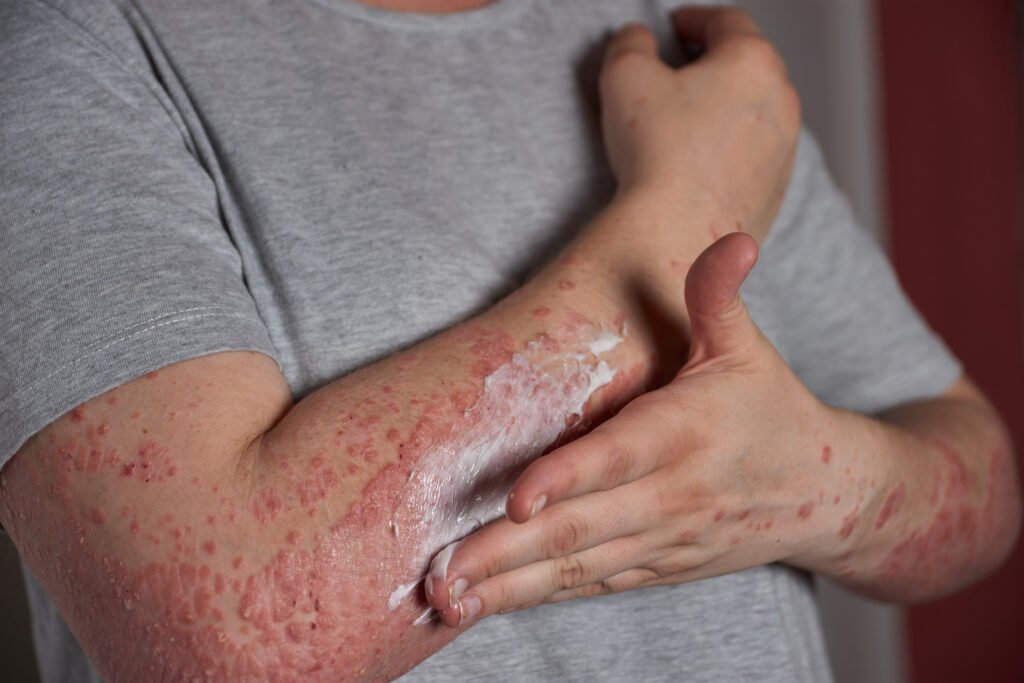
Identification of the viral rash:
The first step in effective treatment is accurate identification. Viral rashes can be caused by a multitude of viruses, including the common cold, influenza, measles, chickenpox, and more. Recognizing the specific virus responsible for the rash aids in tailoring treatment strategies.
Symptomatic Relief:
Addressing the symptoms associated with viral rashes is a key component of management. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help alleviate itching, while pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can reduce discomfort and fever. Cool compresses and soothing lotions, such as calamine, can provide additional relief.
Antiviral Medications:
In some cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed to target the underlying viral infection. For example, medications like acyclovir are effective against the herpes simplex virus, which can cause painful and recurrent rashes. Timely initiation of antiviral therapy is often crucial to its success.
Topical Treatments:
Topical corticosteroids can be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching associated with certain viral rashes. However, their use should be carefully monitored, as prolonged or inappropriate application can lead to skin thinning and other complications.
Hydration and Rest:
Ensuring proper hydration and adequate rest is essential during any viral infection. Adequate fluid intake helps the body fight the infection and maintain overall health, while rest allows the immune system to work more efficiently.
Isolation and Prevention:
Many viral rashes are highly contagious, necessitating isolation to prevent the spread of the infection. Following proper hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Vaccination:
Prevention is always better than cure. Vaccination against certain viral infections, such as measles, mumps, rubella, and chickenpox, is a highly effective way to reduce the incidence of associated rashes. Staying up-to-date with vaccinations is a crucial aspect of public health.
Monitoring and Follow-Up:
Regular monitoring of the viral rash’s progression is essential. If there is no improvement or if the symptoms worsen, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers ensure that the treatment plan is effective and can be adjusted if necessary.
