Introduction
Yeast infections are a common and often misunderstood health concern, affecting millions of individuals globally. These infections, caused by the overgrowth of the Candida fungus, can occur in various parts of the body, leading to discomfort and potential complications. This article aims to shed light on yeast infection, providing a comprehensive understanding of their causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of yeast infections is crucial for both prevention and effective management. While yeast infections are generally treatable, a lack of awareness can lead to recurrent episodes, compromising an individual’s quality of life. By delving into the intricacies of yeast infections, one can empower themselves with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding Yeast Infections
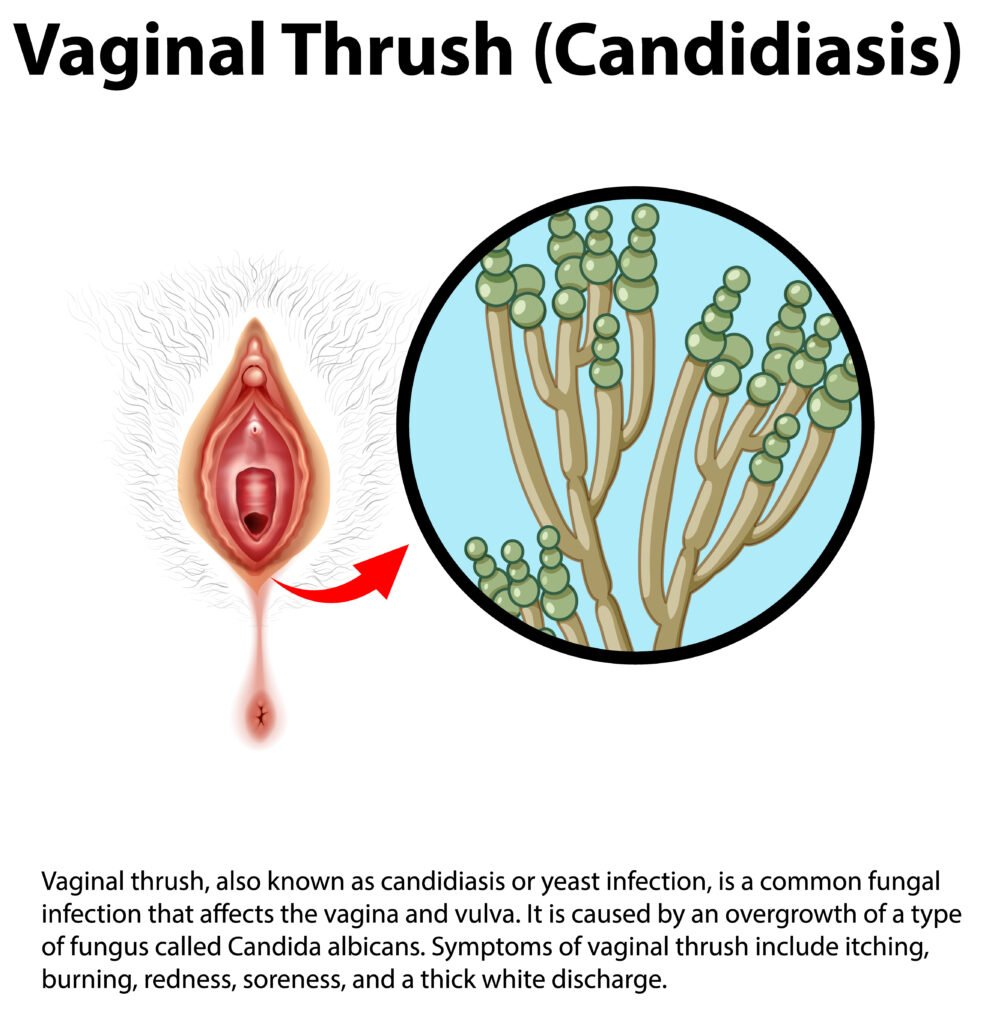
Yeast infections, scientifically known as candidiasis, encompass a range of fungal infections caused by the Candida genus. While the most prevalent form is vaginal yeast infection, other types include oral thrush, skin infections, and invasive candidiasis affecting internal organs. Understanding the diverse manifestations of yeast infections is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Common Causes of Yeast Infections
Candida Overgrowth
The primary culprit behind yeast infection is an overgrowth of Candida, a naturally occurring fungus in the body. Imbalances in the microbiota, often triggered by factors like a weakened immune system or the use of certain medications, can lead to unchecked Candida proliferation.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, are more susceptible to yeast infections. A robust immune response is essential for keeping Candida in check, and any compromise in this defense mechanism can lead to increased vulnerability.
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can create an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth. Understanding the role of hormones in yeast infections is crucial for tailoring preventive strategies for individuals experiencing hormonal shifts.
Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics, while effective in treating bacterial infections, can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body. This disruption often includes the suppression of beneficial bacteria that help control Candida. Consequently, antibiotic use is a common predisposing factor for yeast infections.
Risk Factors for Developing Yeast Infections
Gender-Related Factors
Certain yeast infections, such as vaginal yeast infections, are more common in women. Understanding gender-related risk factors is essential for targeted prevention and early intervention strategies.
Medical Conditions
Pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS, can compromise the body’s ability to fend off infections, increasing the likelihood of yeast infections. Awareness of these risk factors is vital for individuals managing chronic health conditions.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, including diet, hygiene practices, and clothing preferences, can impact the likelihood of developing yeast infections. Addressing these factors proactively can contribute to a holistic approach to preventing and managing yeast infections.
Understanding and Recognizing Yeast Infection Symptoms: A Guide to Early Detection and Medical Attention

Yeast infections are a common occurrence, affecting various parts of the body. Recognizing the symptoms early on is crucial for prompt and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the common symptoms of yeast infections, the importance of early detection, and when it’s essential to seek medical attention.
Common Symptoms of Yeast Infection:
Vaginal Yeast Infection Symptoms: Vaginal yeast infections are among the most prevalent types. Symptoms may include:
- Itching and irritation in the vaginal area
- Abnormal vaginal discharge, often thick and white
- Burning sensation during urination or intercourse
- Redness and swelling of the vulva
Oral Yeast Infection Symptoms: An oral yeast infection, also known as thrush, can manifest in the mouth. Common symptoms include:
- White, creamy patches on the tongue and inner cheeks
- Soreness and redness in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or the sensation of a cottony feeling in the mouth
- Cracking and redness at the corners of the mouth
Skin Yeast Infection Symptoms: Yeast infections can also affect the skin, leading to symptoms such as:
- Red, itchy rash with well-defined borders
- Small, raised bumps or pustules
- Skin peeling or flaking
- Discomfort and irritation in the affected areas
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of yeast infection symptoms is crucial for several reasons:
Effective Treatment: Prompt recognition allows for timely treatment, preventing the infection from worsening.
Prevention of Complications: Untreated yeast infections can lead to complications, such as recurrent infections or the spread of the infection to other parts of the body.
Improved Quality of Life: Addressing symptoms early can alleviate discomfort and improve overall well-being.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some yeast infections can be managed with over-the-counter treatments, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional in the following situations:
Recurrent Infections: If you experience frequent yeast infections, it may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
Severe Symptoms: Intense itching, pain, or swelling may suggest a more severe infection that requires prescription medications.
Pregnancy: Pregnant individuals should seek medical advice before self-treating it.
Read Also: HIIT Workouts: Unleashing the Power of High-Intensity Training
Navigating the Path to Relief: A Comprehensive Guide to the Diagnosis of Yeast Infections
Medical Evaluation and History:
One of the primary steps in diagnosing a yeast infection involves a medical evaluation and a detailed patient history. Healthcare professionals often ask about symptoms such as itching, burning, and unusual discharge. The location and severity of symptoms play a key role in determining the likelihood of a yeast infection. Additionally, factors like recent antibiotic use, compromised immune systems, and hormonal changes may contribute to the development of these infections.
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures:
For a definitive diagnosis, healthcare providers may recommend laboratory tests and diagnostic procedures. A microscopic examination of a sample taken from the affected area, commonly known as a wet mount, allows professionals to identify the presence of yeast cells. Cultures may also be performed to grow and analyze yeast samples, aiding in the identification of the specific strain causing the infection. In some cases, molecular tests such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) may be employed for rapid and accurate detection.
Self-Diagnosis and Over-the-Counter Options:
While seeking professional medical advice is crucial for an accurate diagnosis, some individuals may opt for self-diagnosis based on their symptoms. Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal medications, available in various forms such as creams, suppositories, and oral tablets, can be purchased without a prescription. These medications contain active ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, or fluconazole, which are effective against yeast infections. However, it is important to note that self-diagnosis may lead to misidentification of the condition, and consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for confirmation and appropriate guidance.
Yeast Infections: Effective Treatment Strategies

Yeast infection, caused by the overgrowth of the Candida fungus, can be both uncomfortable and persistent. While conventional medical treatments are widely available, many individuals seek alternative approaches, including natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments. In this article, we will explore various treatment strategies categorized into conventional medical treatments, natural and home remedies, and lifestyle adjustments for prevention.
Conventional medical treatments:
Antifungal Medications:
Antifungal medications are commonly prescribed to combat yeast infections. These drugs work by inhibiting the growth of the Candida fungus, ultimately eliminating the infection.Examples of antifungal medications include fluconazole, clotrimazole, and miconazole.
Topical Creams and Ointments:
Topical treatments are often used to alleviate the symptoms of yeast infection, providing relief from itching and irritation.Creams and ointments containing antifungal agents can be applied directly to the affected area for localized treatment.
Can sudocrem help with yeast infections?
Sudocrem is primarily designed as a topical antiseptic and healing cream, often used to soothe and protect irritated skin. While it may offer relief for certain skin conditions, it is not specifically formulated to treat yeast infections. A yeast infection is typically caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungus and is best addressed with antifungal medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. Although some individuals may find temporary comfort in the soothing properties of Sudocrem, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for yeast infections.
Natural and home remedies
Probiotics:
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that promote a healthy balance in the gut flora. They can help prevent and treat yeast infections by restoring the natural microbial balance.Consuming probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, or taking probiotic supplements, can be beneficial.
Dietary Changes:
Dietary modifications can play a crucial role in managing yeast infection. Limiting the intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates, which can contribute to yeast overgrowth, is essential.Emphasizing a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can support overall health and help prevent recurrent infections.
Herbal Treatments:
Certain herbs possess antifungal properties that may aid in combating yeast infections. Examples include garlic, tea tree oil, and oregano oil.These herbal treatments can be used topically or incorporated into the diet, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying herbal remedies.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Prevention
Hygiene Practices:
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial for preventing yeast infection. Practice regular and gentle cleansing of the genital area, using mild, unscented soaps.Avoid douching, as it can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the vagina.
Clothing Choices:
Choose breathable fabrics, such as cotton, to allow adequate airflow. Avoid tight-fitting clothing that can trap moisture, creating an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth.
Sexual Practices:
Practicing safe sex and communicating openly with sexual partners can contribute to preventing recurrent yeast infections. Consider using water-based lubricants without added sugars, as sugars can promote yeast growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grappling with a yeast infection can be a discomforting chapter in one’s health journey, but understanding its nuances and seeking appropriate care can pave the way for relief. Whether opting for over-the-counter remedies or consulting a healthcare professional for personalized guidance, acknowledging the body’s signals is paramount. Embracing preventive measures, such as maintaining a balanced diet and practicing good hygiene, can significantly contribute to thwarting future occurrences. While yeast infection may be an unwelcome visitor, the power to manage and overcome it lies within informed choices and proactive health practices.
