Introduction
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a critical medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of congestive heart failure, including its definition, causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. By delving into the intricate details of this condition, we hope to empower readers to recognize the signs, manage risk factors, and seek timely medical intervention.
Congestive Heart Failure
CHF is a chronic medical condition characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently, leading to a buildup of fluid in the lungs and other tissues. This condition can result from various cardiovascular issues, affecting the heart’s ability to meet the body’s demands for oxygen and nutrients.
Congestive Heart Failure: Causes and Treatment Options
Understanding the causes and treatment options for CHF is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows individuals to recognize potential risk factors and take proactive measures to prevent or manage the condition. Secondly, early detection and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with congestive heart failure.
Causes of Congestive Heart Failure
To comprehend CHF fully, it’s essential to explore its underlying causes. This section will discuss both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, as well as the role of underlying health conditions in contributing to the development of CHF.
Risk Factors
Various risk factors can contribute to the development of CHF. These may include lifestyle choices such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle. Additionally, conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity can increase the risk of developing CHF.
Underlying Health Conditions
Several underlying health conditions can contribute to CHF, including coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction (heart attack), valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. Understanding the interplay of these conditions is crucial for both prevention and targeted treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of CHF is vital for early intervention. In this section, we will explore the common signs and symptoms of CHF, as well as the diagnostic tests and procedures used by healthcare professionals to confirm a diagnosis.
Common Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure manifests through a range of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen legs or ankles, and persistent coughing. Understanding these symptoms and their potential variations is key to identifying the condition in its early stages.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
An accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. This section will delve into the various diagnostic tests and procedures used to assess heart function, including echocardiograms, stress tests, and blood tests. Understanding these diagnostic tools empowers individuals to actively participate in their healthcare.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, individuals with congestive heart failure have several treatment options available to them. This section will explore pharmaceutical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and surgical procedures commonly used to manage CHF.
Medications
A variety of medications can help manage congestive heart failure. These may include diuretics to reduce fluid retention, ACE inhibitors to relax blood vessels, and beta-blockers to improve heart function. Understanding the purpose and potential side effects of these medications is crucial for individuals managing CHF.
Lifestyle Changes
Beyond medications, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing congestive heart failure. This includes adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and quitting smoking. These changes not only enhance overall well-being but also contribute to better heart health.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address underlying issues contributing to CHF. This may involve procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or heart valve repair or replacement. Understanding these surgical options allows individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Managing Congestive Heart Failure
Effectively managing congestive heart failure requires a comprehensive approach that extends beyond medical interventions. This section will provide practical tips for self-care, symptom management, and the importance of regular check-ups and monitoring.
Tips for Self-Care and Symptom Management
Individuals living with CHF can take proactive steps to manage their condition. This may include adhering to prescribed medications, monitoring fluid intake, and recognizing early signs of worsening symptoms. Practical self-care tips can significantly contribute to a better quality of life.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups are crucial for individuals with CHF. This section will emphasize the importance of ongoing monitoring, including routine appointments with healthcare providers, regular heart function assessments, and timely adjustments to treatment plans. This proactive approach enhances the effectiveness of CHF management.
Read Also: Back Pain Relief: Unveiling Effective Strategies for a Pain-Free Life
Congestive Heart Failure leg cramps:
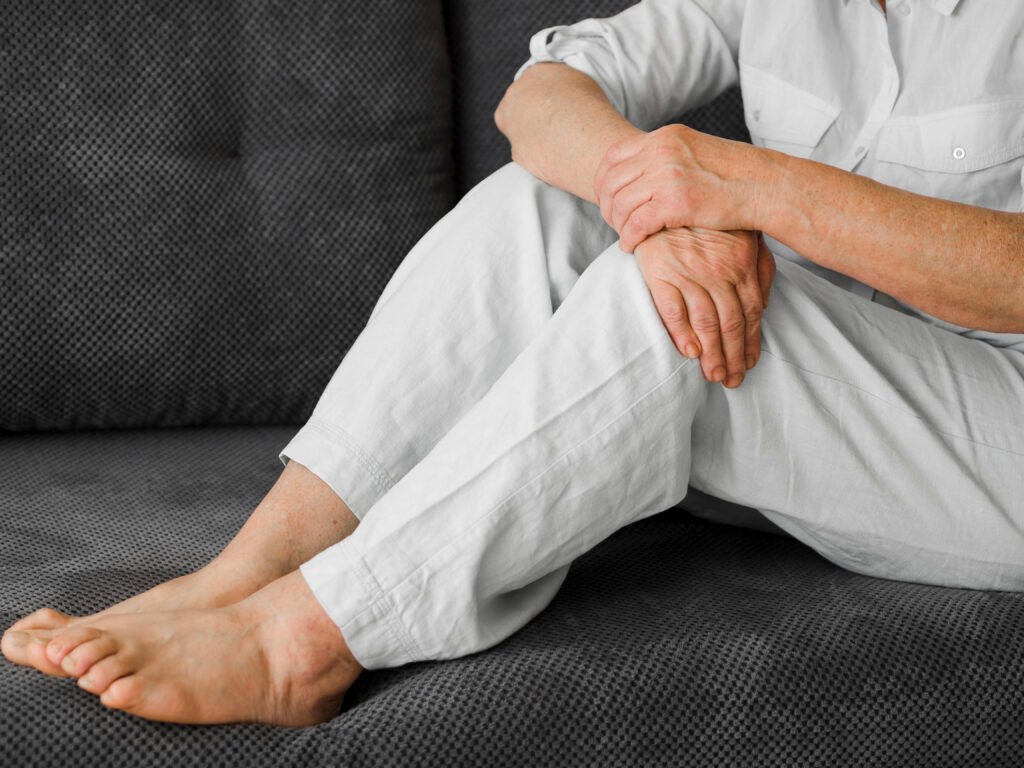

Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to a buildup of fluid in the lungs and other parts of the body. While the primary symptoms of CHF are related to the cardiovascular system, individuals with this condition may also experience symptoms in other parts of their bodies, such as the legs. Leg cramps are a common complaint among those with congestive heart failure, and understanding the connection between the two is crucial for effective management.
The Link Between CHF and Leg Cramps:
Leg cramps in individuals with congestive heart failure can be attributed to several factors. One of the primary causes is fluid retention. As the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently, fluid can accumulate in the legs, leading to swelling and discomfort. This fluid buildup can also put pressure on nerves, contributing to the occurrence of leg cramps.
Electrolyte imbalances, which are common in CHF patients, can also play a role in the development of leg cramps. The heart’s compromised ability to circulate blood may impact the distribution of electrolytes, such as potassium and sodium, throughout the body. This imbalance can result in muscle cramping and spasms.
Medications used to manage CHF can further contribute to the likelihood of leg cramps. Diuretics, commonly prescribed to reduce fluid retention, may lead to electrolyte imbalances, exacerbating cramping in the legs.
Congestive Heart Failure: Conclusion

In conclusion, congestive heart failure is a complex medical condition with significant implications for affected individuals. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for early detection and effective management. By adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, medications, and, when necessary, surgical interventions, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite living with CHF.
Early detection of congestive heart failure can significantly impact outcomes. Timely intervention and proper management can improve symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance the overall quality of life. This section will underscore the critical role of early detection and stress the importance of seeking medical advice promptly.
Call-to-Action
As a final call-to-action, readers are encouraged to seek medical advice if they experience any symptoms or possess risk factors related to heart failure. Early intervention and proactive management can make a substantial difference in the course of this condition, promoting better health and well-being. If you or someone you know is at risk or exhibiting symptoms, don’t hesitate—schedule a consultation with a healthcare professional today. Your heart health matters, and taking action now can pave the way for a healthier future.
