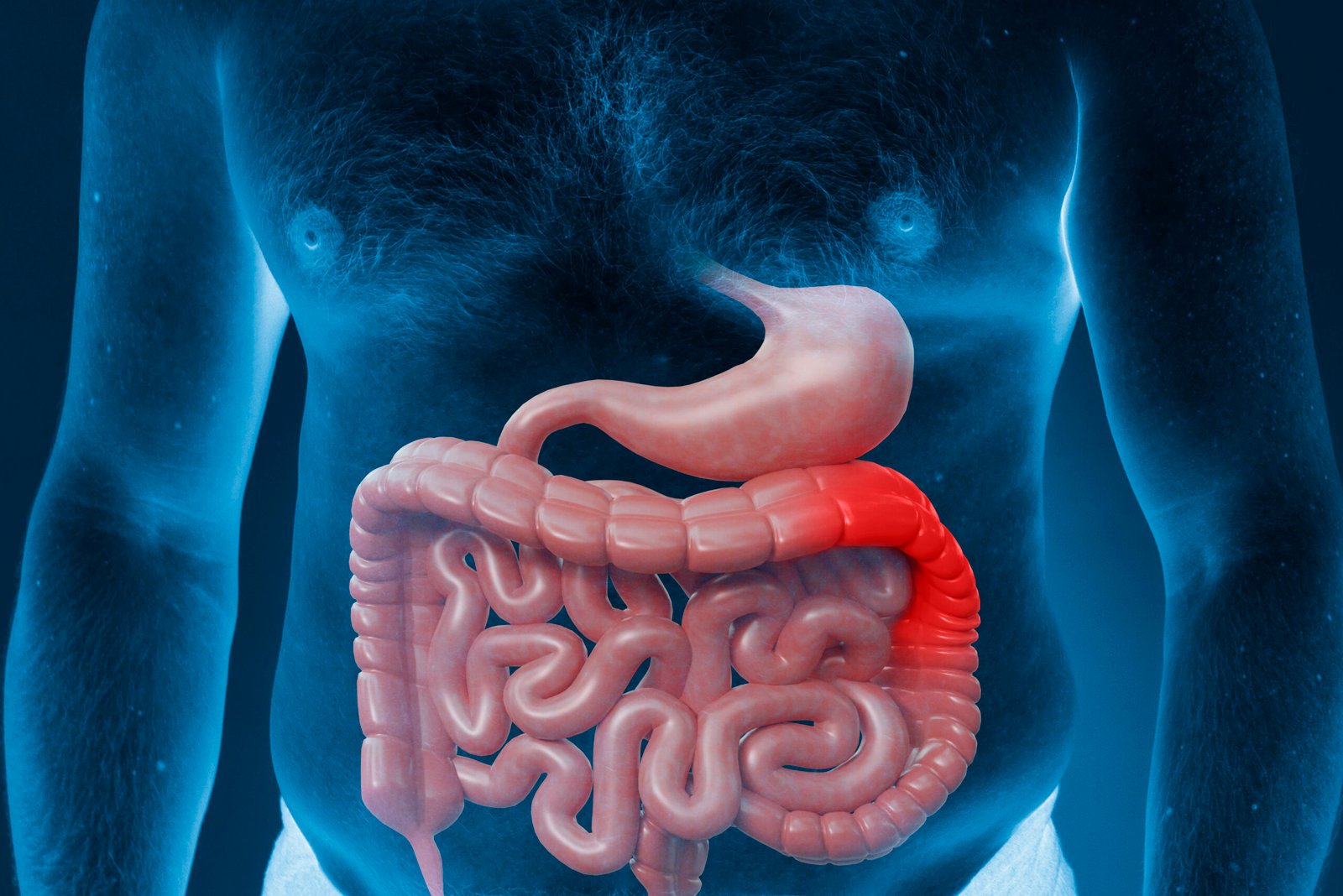
Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by inflammation of the colon and rectum, leading to the formation of ulcers and various symptoms. It is considered an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the large intestine, causing inflammation and tissue damage. The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Understanding the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon and rectum, causing a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While the exact cause of UC remains unknown, a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors is believed to contribute to its development. Recognizing the symptoms of UC is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Here, we will explore some common signs that may indicate the presence of ulcerative colitis.
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort:

One of the hallmark symptoms of UC is abdominal pain or discomfort. This pain is often crampy and can vary in intensity. Individuals with UC may experience pain in different parts of the abdomen, depending on the location and extent of inflammation in the colon.
Diarrhea:
Frequent and urgent bowel movements, often accompanied by diarrhea, are common symptoms of UC. The inflammation in the colon leads to the rapid transit of stool through the intestines, resulting in loose and watery bowel movements. In severe cases, individuals may experience bloody diarrhea, indicating inflammation and ulceration of the colon lining.
Rectal Bleeding:
Blood in the stool or on toilet paper after bowel movements is a significant red flag for ulcerative colitis. The inflammation in the colon can cause ulcers, leading to bleeding. The color of the blood can range from bright red to darker shades, depending on the severity and location of the inflammation.
Weight loss and fatigue:
Chronic inflammation and frequent bowel movements can lead to weight loss and fatigue in individuals with UC. The body may struggle to absorb nutrients properly, and the persistent symptoms can take a toll on energy levels.
Anemia:
Prolonged inflammation and bleeding in the colon can lead to a decrease in red blood cells, causing anemia. Anemic individuals may experience weakness, fatigue, and pale skin. Regular monitoring of blood counts is essential for managing UC and preventing complications related to anemia.
Joint pain and inflammation:
Some individuals with UC may experience joint pain and inflammation, a condition known as peripheral arthritis. These symptoms are believed to be related to the immune system’s response to inflammation in the colon.
Skin and Eye Problems:
In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, UC can manifest with skin rashes, lesions, or eye inflammation. These extraintestinal manifestations may occur in some individuals with ulcerative colitis.
Recognizing the symptoms of ulcerative colitis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of the condition. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, or other concerning symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can conduct diagnostic tests and develop a personalized treatment plan to help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals living with ulcerative colitis.
Exploring Effective Treatment Strategies for Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, inflammatory bowel disease characterized by inflammation of the colon and rectum. Managing this condition requires a comprehensive approach that combines medication, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes surgical intervention. In this article, we will delve into the various treatment strategies employed to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with ulcerative colitis.
Ulcerative Colitis: Medication
Aminosalicylates:
These anti-inflammatory drugs, such as mesalamine and sulfasalazine, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the colon. They can be administered orally or as rectal suppositories, depending on the location and severity of the inflammation.
Corticosteroids:
In cases of moderate-to-severe inflammation, corticosteroids like prednisone may be prescribed to quickly suppress the immune response. However, long-term use is generally avoided due to potential side effects.
Immunomodulators:
Drugs like azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine work by suppressing the immune system to reduce inflammation. They are often used in cases where aminosalicylates and corticosteroids have proven ineffective.
Biologics:
More recently, biologic medications such as infliximab, adalimumab, and vedolizumab have shown efficacy in targeting specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process.
Ulcerative Colitis: Lifestyle Modifications

Stress management:
Stress does not cause ulcerative colitis, but it can exacerbate symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and counseling may help manage stress levels.
Diet:
While diet alone cannot cure ulcerative colitis, certain dietary changes may help manage symptoms. Some individuals find relief by avoiding certain trigger foods, such as spicy foods, dairy, and high-fiber foods, during flare-ups.
Regular exercise:
Research has shown that physical activity positively impacts gut health. However, it’s important to tailor exercise routines to individual capabilities and avoid excessive strain.
Surgical Interventions:
In cases where medications and lifestyle adjustments do not provide sufficient relief or in emergencies such as perforation or uncontrollable bleeding, surgery may be recommended. The most common surgical option is a colectomy, which involves removing part or all of the colon. In some cases, this procedure may be curative.
Ulcerative colitis is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. While medications play a crucial role in managing inflammation, lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, surgery are essential components of a comprehensive treatment strategy. It is important for individuals with ulcerative colitis to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and challenges. Ongoing research continues to explore new therapeutic options, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those living with ulcerative colitis.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure: Understanding Causes and Treatment
Nourishing Resilience: A 7-Day Meal Plan for Ulcerative Colitis

Living with ulcerative colitis requires a thoughtful and tailored approach to nutrition. The right diet can significantly impact the management of symptoms, promoting gut health and overall well-being. Crafting a 7-day meal plan for ulcerative colitis involves selecting foods that are gentle on the digestive system while providing essential nutrients. Let’s explore a nourishing and delicious meal plan designed to support individuals with ulcerative colitis over the course of a week.
1st:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with mashed bananas and a sprinkle of chia seeds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken with quinoa and steamed carrots.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with sweet potato and spinach
2nd:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt parfait with berries and a drizzle of honey.
- Lunch: Turkey and avocado wrap with a side of mixed greens.
- Dinner: stir-fried tofu with brown rice and broccoli.
3rd:
- Breakfast: Smoothie with spinach, pineapple, and almond milk.
- Lunch: lentil soup with a side of whole-grain crackers.
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with quinoa and roasted zucchini.
4th:
- Breakfast: scrambled eggs with sautéed spinach and whole-grain toast.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and feta cheese.
- Dinner: Baked chicken with sweet potato wedges and green beans.
5th:
- Breakfast: Cottage cheese with sliced peaches and a handful of walnuts.
- Lunch: brown rice bowl with black beans, salsa, and avocado.
- Dinner: Cod fish with couscous and steamed asparagus.
6th:
- Breakfast: Chia seed pudding with mixed berries.
- Lunch: Grilled vegetables with hummus and whole-grain pita.
- Dinner: Turkey meatballs with quinoa and roasted Brussels sprouts.
7th:
- Breakfast: banana and almond butter smoothie.
- Lunch: spinach and feta-stuffed chicken breast with a side of roasted sweet potatoes.
- Dinner: stir-fried tempeh with brown rice and mixed vegetables.
General Guidelines:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay well-hydrated and support digestion.
- Fiber: Include soluble fiber-rich foods like oats, bananas, and sweet potatoes to help regulate bowel movements.
- Protein: Opt for lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, tofu, and eggs to support muscle health.
- Probiotics: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt to promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
- Avoid Triggers: Steer clear of known trigger foods, such as spicy dishes, caffeine, and high-fat items.
Crafting a 7-day meal plan for ulcerative colitis involves a delicate balance of nourishing and soothing foods. This plan aims to provide a variety of nutrients while being mindful of triggers that may exacerbate symptoms. Remember, individual responses to foods can vary, so it’s crucial to listen to your body and work closely with healthcare professionals to refine and adjust your meal plan as needed. With the right approach, a well-balanced diet can be a powerful ally in managing ulcerative colitis and enhancing overall quality of life.
Ulcerative Colitis: Conclusion

Ulcerative colitis poses a formidable challenge, but with a nuanced understanding of its symptoms and treatment options, individuals can collaborate with healthcare providers to formulate effective management plans. By exploring the intricate facets of abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue and delving into the diverse treatment strategies encompassing medication, surgery, and dietary changes, this article aims to empower those grappling with ulcerative colitis to navigate their journey towards a healthier, more manageable life.